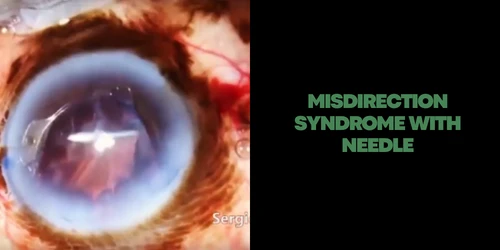
ACUTE MISDIRECTION SYNDROME
Characterized: anterior chamber very shallow, with absence of supracoroidian effusion or hemorrhage and without perceptible pathology in iris-lens diaphragm. It usually relieves phacoemulsification without intercurrences in hypermetropic eyes. Pathophysiology: Inadequate movement of balanced saline solution (BSS) through the zonular fibers that accumulate, therefore in the posterior segment generating an increase in posterior pressure, resulting in anterior displacement of the iris-lens diaphragm, axial and anterior peripheral chamber flattening and secondary angular closure. It is normally occurred in the end of the phacoemulsification. Facing such situations, pars plana decompression is necessary, but one should first be sure that there is no evidence of choroidal effusion or bleeding.
Decompression may be done by puncture with a straight 26G insulin needle 3 mm from the limbus followed by aspiration of the fluid posterior to the bag or using a vitrectomy trocater (caliber 23, 25 or 27) to remove retrocapsular fluid using a high shear rate.